Pubic hair removal is not a new trend. In fact, the practice dates back to ancient Egypt and Greece, where women—particularly those in certain professions—were expected to shave for hygiene and social identification purposes.
While female body hair removal became mainstream between 1915 and 1945, the removal of pubic hair didn’t become popular until the 1980s. Today, it’s common practice, but recent studies show that 60% of women who groom their pubic region experience at least one health-related issue. The most frequent complications include epidermal abrasions (tiny, often invisible skin cuts) and ingrown hairs, both of which can lead to skin irritation, infections, and increased risk of transmitting sexually transmitted infections (STIs).
Important Reasons Not to Shave Your Pubic Hair
1. Pubic Hair Helps Regulate Body Temperature
Body hair, including pubic hair, plays a vital role in thermoregulation. Each hair follicle contains a sebaceous gland that releases oil. This oil travels to the skin’s surface, and when it evaporates, it helps cool the body through latent heat release.
2. Natural Protection Against Infections and Irritants
Pubic hair serves as a barrier against harmful bacteria, dirt, and other foreign particles. By keeping these irritants at bay, it helps reduce the risk of infections and skin conditions in the genital area.
3. Pubic Hair Traps Pheromones
Pheromones—chemicals responsible for sexual attraction—are absorbed in areas with body hair. The sweat glands around the pubic region release these secretions, and pubic hair helps retain them, playing a subtle role in attraction.
4. Higher Risk of Genital Warts
Shaving increases the likelihood of developing genital warts, which appear as small, flesh-colored bumps around the genital area. Many people don’t realize they have them, and shaving can irritate the skin and make it easier for the virus to spread.
5. Increased Chance of Contracting Molluscum Contagiosum
Molluscum contagiosum is a contagious viral skin infection that can be transmitted through close contact. Hair removal, particularly shaving, can cause micro-abrasions that make it easier for the virus to enter the skin. Research shows a stronger link between shaving and this infection, as scratching irritated areas can lead to autoinfection.
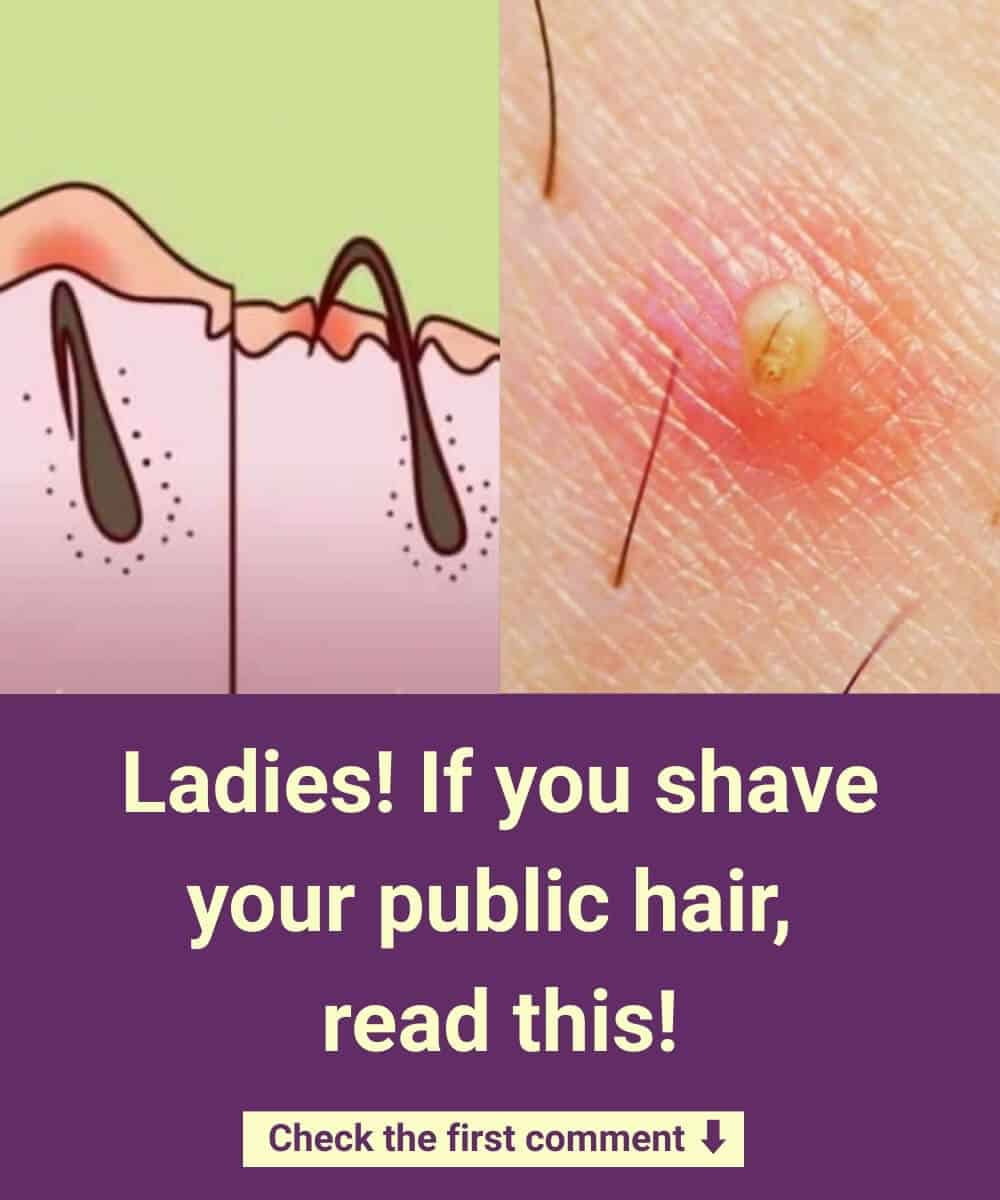
6. Skin Irritation and Long-Term Damage
Shaving frequently causes trauma to hair follicles, leaving behind small wounds. Maintaining smooth skin requires repeated grooming, which leads to ongoing irritation, razor burn, and redness in sensitive areas. Many doctors report seeing patients with boils, abscesses, and even cellulitis due to shaving in the genital region.
7. Obese and Overweight Women Face Greater Risks
According to a U.S. study, complications from pubic hair removal are nearly double for overweight women and triple for those who remove all pubic hair. This is primarily because skin in these areas tends to be more tightly packed, increasing the chances of friction, ingrown hairs, and infections.
Final Thoughts
Although grooming is a personal choice, it’s essential to understand the potential risks involved with pubic hair removal. From skin irritation and infections to increased vulnerability to STIs, shaving this sensitive area can have more serious health consequences than many realize. Being informed can help you make a safer and healthier decision for your body.